Publications
Optical calibration to ensure accuracy

More metrological performance
Qualimatest has developed and integrated into its software an algorithm which allows, depending on the optical system (the camera, lens and lighting assembly), to perform an absolute calibration of the system. To do this, Qualimatest characterizes the optical components of its equipment to determine their optical chain transfer function. The software of the QMTMesure family corrects the image by compensating for imperfections in the optical chain to provide an "accurate" measurement.
QMTMesure softwareThe telecentric is good, with QMTJust it is better
Unlike standard optical systems with which the image size changes proportionally with respect to the distance between the object and the lens, with telecentric optics, the size of the object theoretically remains constant with respect to the distance. This is the main reason for the popularity of telecentric systems in machine vision. A telecentric optical system and its beams almost parallel to the optical axis:
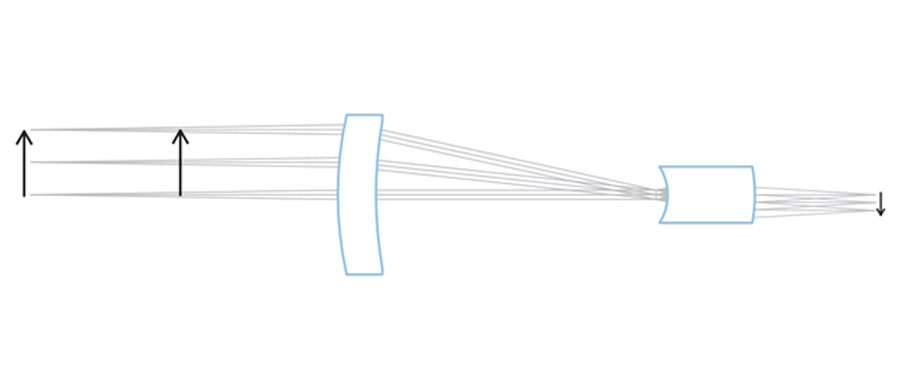
However, it should not be forgotten that telecentric optics also induce "magnification errors", even if the latter is 10 or 100 times less than with a standard optical system. In a telecentric lens, the change in magnification is determined by the “telecentric slope” expressed in degrees or radians. A good telecentric lens has an effective telecentric slope of about 0.1 ° (0.0017 rad); this means that the dimensions of the object change by 1.7µm for every 1mm displacement. A relative calibration with respect to a reference makes it possible to transform the pixels into physical dimensions (often in millimeters) and correct, up to optical non-linearities, magnification errors and distortions. On the other hand, the non-linearities and the errors caused by the fact that the lights are not perfectly coherent cannot be compensated by a relative calibration (offset).
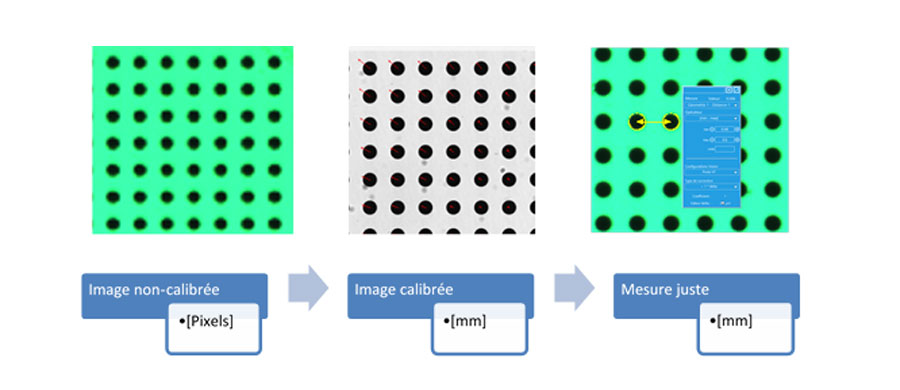
Qualimatest has set up a procedure that allows, depending on the vision setup (the camera, lens and lighting assembly), to perform an absolute calibration of the system. To do this, Qualimatest characterizes the optical components of its equipment to determine their optical chain transfer function. The software of the QMTMesure family corrects the image by compensating for imperfections in the optical chain to provide an "accurate" measurement. The calibration procedure proposed by Qualimatest and schematized below:
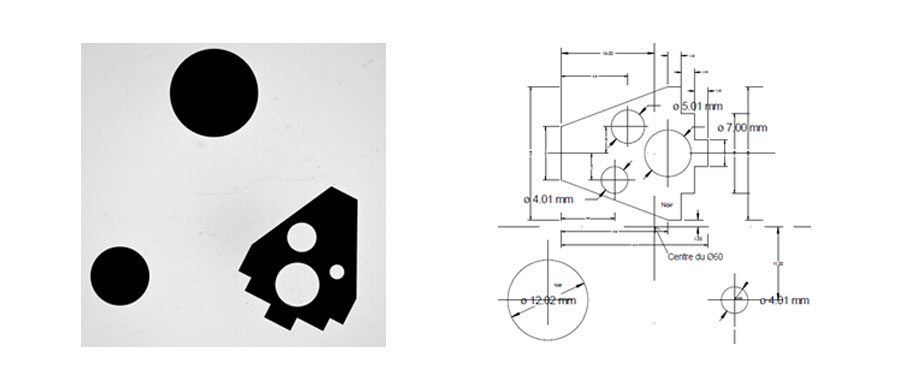
To validate this method, references measured by the Federal Institute of Metrology in Switzerland, METAS, were used. One of these references is illustrated below. Of the three references used, 9 internal diameters, 6 external diameters and two lengths were measured:
The deviations from the METAS values are compared between the measurements with only a relative calibration (unadjusted), the measurements adjusted with a simple offset and those adjusted by Qualimatest (QMTJust)
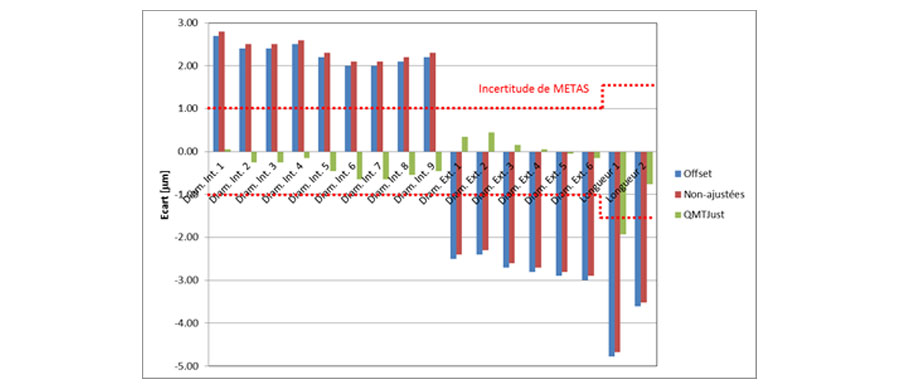
The measurement uncertainties reported by METAS are ± 1µm, for diameters, and ± 1.5µm, for lengths. Measurements corrected with QMTJust are, on average, 16 times more accurate than those with a standard calibration. In some cases, QMTJust reduced the measurement accuracy error by a factor of> 50. This is, for example, the case of outside diameter number 5. The deviation after standard calibration with METAS is 2.8µm, but it is reduced to 0.05µm with QMTJust.
- Improved measurement accuracy: 16x
- Accuracy of measurement errors << to 1µm




